In cooking, different types of onions are used - onions, green, leeks, shawls, chives, batun. What does onion-batun look like, how is it grown, eaten and stored, you will find answers to these and other common questions by reading the article.
What is the onion-batun
Onion-batun is a herbaceous perennial that is reckoned with the Onion family and the Asparagus order. Presumably his homeland is Asia. In the wild, it is now found in Japan, China and Siberia. The plant has 2 more names: Tatar and cod onion. Perennial forms oblong bulbs, but they may be completely undeveloped. The hollow stem grows to a height of 1 m. 5-7 fist leaves are formed on it. During flowering, a multifloral umbrella appears in the form of a ball. Flowers are placed on thin pedicels. Perianth in the form of yellow bells.
Onion greens or an entire vegetable plant is used: it is rich in carotene, sugars, vitamins C, B1, B2, nicotinic acid, essential oil, potassium salts, magnesium, iron, and volatile products. The green parts of the rod contain 2 times more ascorbic acid than the green onions. Due to its rich chemical composition, onion-batun has a number of useful properties on the human body, the main ones being strengthening immunity, satisfying stomach pain, improving kidney function and the state of blood vessels. It is used in traditional and traditional medicine as a means of lowering blood pressure, increasing the elasticity of capillaries, providing a diaphoretic, tonic and analgesic effect. Despite the benefits to human health, the onion-batun can also be harmful. It is not recommended for people with such diagnoses - stomach ulcers, gastritis, pancreatitis.
It is used in traditional and traditional medicine as a means of lowering blood pressure, increasing the elasticity of capillaries, providing a diaphoretic, tonic and analgesic effect. Despite the benefits to human health, the onion-batun can also be harmful. It is not recommended for people with such diagnoses - stomach ulcers, gastritis, pancreatitis.
It is better for healthy people not to eat the described vegetable plant in large quantities at a time. In cooking, batun is added to various dishes, sauces, salads, marinades, and used as a seasoning. Fresh, its taste is very reminiscent of onions, but it is softer and more tender. Its nutritional value is higher and amounts to 35 kcal per 100 g, it contains 1.3 g of protein, 0.1 g of fat, 3.2 g of carbohydrates.
Did you know? The beneficial properties of onions have been known since the time of Hippocrates (460 BC. – 370 g.). The vegetable was prescribed by the military to strengthen immunity, increase strength; It was also recommended for getting rid of rheumatism, gout, obesity.
The following varieties are most often grown in open ground:
- April. A variety of Japanese variety. Harvest can be harvested early. The plant is resistant to low temperatures and diseases.

- Russian winter. Matures in the medium term. It has strongly branching leaves 50 cm long. Their taste is slightly sharp.

- Tenderness. Mid-season salad grade. It is characterized by high productivity. Forms leaves covered with a wax coating, 40 cm long.

- Performer. Forms juicy leaves 50 cm long. Their taste is slightly sharp.

- Emerald. Hybrid early ripening. Able to withstand cold temperatures. It has a good resistance to disease. Leaves are covered with wax coating.

- Red snowdrop. Matures early. It is characterized by frost resistance. Leaves reach a length of 30 cm. To taste juicy and tender.

- Cipollino. Early ripe high-yielding variety with frost resistance. It has an increased resistance to infection by diseases and pest attacks. The leaves are juicy, slightly sharp. Productivity - 6–6.5 kg / m².

Choosing a place to land
Onion-batun can be easily grown in a summer cottage - neither planting nor caring for it will take much time and effort. Most often, it is grown from seeds that are sown directly in the soil or seedlings are grown from them. Seedling method is used only if you want to harvest in an extremely quick time. Sowing can be done several times during the season: in spring, summer and autumn. First you need to find a good place to land.
Important! The best predecessors for onion-batun are legumes, tomatoes, cabbage, potatoes; worst —– all types of onions, garlic, carrots, cucumbers.
The plant loves good lighting, so the area where it will grow should be adequately lit by sunlight. But direct rays are harmful to greenery, therefore, at noon it is better if the beds are in partial shade, falling, for example, from higher plants. The beds are recommended to be located in the direction to the south or southeast side. Onions do not like the close occurrence of groundwater, therefore, when choosing a place for landing, this peculiarity should be taken into account. The described vegetable plant prefers fertile soil with low or medium pH. It grows well on loam and sandy loam. The soil for planting needs to be prepared in the fall. You will need to make compost and peat (4 kg / 1 m²), a mixture of nitrate (10 g), potassium chloride (10 g), superphosphate (30 g) for digging.
The described vegetable plant prefers fertile soil with low or medium pH. It grows well on loam and sandy loam. The soil for planting needs to be prepared in the fall. You will need to make compost and peat (4 kg / 1 m²), a mixture of nitrate (10 g), potassium chloride (10 g), superphosphate (30 g) for digging.
Seed preparation before planting
Seed must be soaked for 24 hours in any growth stimulator, and then well dried to make it loose.
Seeding time
The first sowing of seed material is carried out in early May, when the threat of freezing frost will pass. Germination is possible at a temperature of + 3 ° C. To get a second crop, the seeds are sown in the summer - in June - July. For the third time, onions can be sown in the winter - in October - November. When sowing between beds, they maintain a distance of 25 cm, between holes with seeds - 10–15 cm. 1.2 g of seeds (about 320–330 pieces) are sown on 1 m².
In regions with harsh conditions, the sowing density is increased to 3 g. The recommended planting depth is 3 cm. Aisles can be immediately mulched with a layer of humus, straw or mowed grass, and the beds should be covered with non-woven material. Seedlings should be expected 2 weeks after sowing. They immediately need to be thinned, leaving a gap of 2-3 cm between the plants. When re-thinning, leave a distance of 4-6 cm.
Care and cultivation of onion
In order to get a good harvest, it is enough to carry out the minimum set of care measures: water, take care of the soil, apply fertilizers, and carry out preventive treatments against diseases and harmful insects.
Watering mode
Onion-batun loves moisture, so you need to water it often and plentifully. Recommended frequency of hydration - 2 times a week. In the hot period, you can moisturize more often - every other day. The soil should be saturated with moisture 17-19 cm deep. Optimum flow rate - 20 l / m².
Important! Watering should be done with water warmed to room temperature. When moistened with cold water, fungal diseases may develop.
Weeding and cultivating row spacing
For the season 5-6 loosening is required. They are produced a day after irrigation or rainfall. This procedure improves the moisture and air conductivity of the soil and prevents the formation of a hard crust on its surface. As a result, nutrients are delivered faster and in full to the roots of the plant. Loosening can be combined with weeding. It is important to remove weeds in a timely manner so that they do not take away sunlight and nutrients from the onion. To reduce the number of loosening allows mulching. This procedure will limit weed growth and retain moisture in the ground.
Loosening can be combined with weeding. It is important to remove weeds in a timely manner so that they do not take away sunlight and nutrients from the onion. To reduce the number of loosening allows mulching. This procedure will limit weed growth and retain moisture in the ground.
Fertilizer application
Since the batun has the ability to accumulate nitrates, it is recommended to feed it only with organic fertilizers. Suitable slurry, mullein, wood ash, water solution of bird droppings.
Most often, feeding is carried out with mullein mixed with water in a ratio of 1 to 10, or bird droppings in a ratio of 1 to 15. From wood ash can be prepared as an aqueous solution, mixing 1 tbsp. with 10 l of water, and make it in the form of powders in a dry form.
Diseases and Pests
With proper and high-quality agricultural technology, the onion-batun is not affected by diseases and pests. However, if the owner of the site makes mistakes in care, then the plant's immunity can malfunction, as a result of which it will hurt. Of the diseases, onions are most often affected by peronosporosis, or downy mildew. This fungal disease develops at high humidity, characterized by the appearance of a gray-violet coating on the leaves. They treat peronosporosis by spraying the onion with the “HOM” preparation 2-3 times or a solution of copper sulfate with breaks of 10 days.
This fungal disease develops at high humidity, characterized by the appearance of a gray-violet coating on the leaves. They treat peronosporosis by spraying the onion with the “HOM” preparation 2-3 times or a solution of copper sulfate with breaks of 10 days.
Of the pests for a vegetable plant, the greatest danger is:
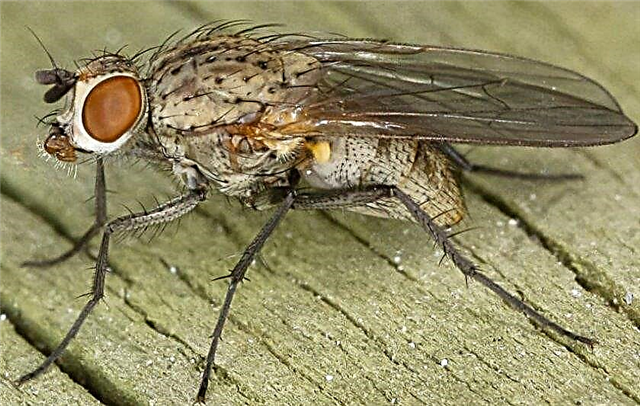
- Onion fly. In appearance it resembles an ordinary gray fly. Its length is 0.6–0.7 cm. The larvae of this insect feed on bulbs. In order to prevent the spread of the pest, a vegetable plant is sprayed 2-3 times with saline (1 tbsp. / 10 l of water), regularly dusted with wood ash, tobacco dust. In case of severe damage, insecticide treatments are used - “Aktara”, “Fly-eater”, “Alatar”.

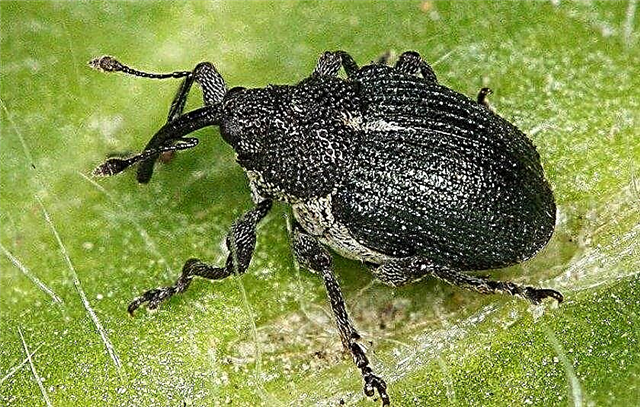
- Onion weevil (secretive worm). This is a small sucking beetle with a gray body and a long proboscis, which feeds on the plant's juices, thereby draining it and leading to death. In order to prevent the appearance of the pest, the beds are sprinkled with black pepper, mustard powder, tobacco dust, wood ash. In case of damage, the plants are sprayed with infusions of tomato, potato tops, Karbofos, Thiophos, and Rogor.

- Onion fire. This is a small butterfly whose larvae eat leaves from the inside. To prevent the appearance of this insect in the garden, it is necessary to spray the plantings with the infusion of mustard powder. During treatment, damaged sheets must be removed and burned. Plants must be treated with insecticides, the active substance of which is bifentrin.

Features of harvesting and storage of crops
When exactly you need to harvest the onion, it will depend on the climatic conditions in the region where it is grown. In areas with a warm and temperate climate, 2-3 crops can be harvested. When grown in harsh conditions, greens are cut once a season. Harvesting a vegetable plant begins a month after the first shoots appear. 1.5 months after harvesting the first crop, green leaves can be re-harvested.
Important! 2-3 days before the planned harvest, the plant should be well watered — it will saturate the foliage with juiciness and make its taste more tender.
The plant is cut off or cut with scissors, leaving a section 5 cm high from the soil. This should be done with extreme caution so as not to stretch the bulb from the ground and not damage the roots. There are several ways you can store onions. Storage of greenery is carried out in boxes or plastic film. It can be stored in the refrigerator for no more than a month. To save it for the winter, freezing is required. The arrows must be washed, cut, packaged in a plastic container or in a plastic bag and placed in the freezer. In this state, the vegetable is suitable for harvest until next year. You can also dry the onion to use later as a seasoning. Dried vegetables should be stored in paper, cloth bags or glass containers with lids. Seasoning shelf life - 2 years.
The arrows must be washed, cut, packaged in a plastic container or in a plastic bag and placed in the freezer. In this state, the vegetable is suitable for harvest until next year. You can also dry the onion to use later as a seasoning. Dried vegetables should be stored in paper, cloth bags or glass containers with lids. Seasoning shelf life - 2 years.
Did you know? At Yale University (USA), the first 3 cookbooks are stored in the form of tablets. They describe the tradition of the ancient Mesopotamians to use various types of onions.
So, due to the fact that the onion-batun is characterized by unpretentiousness in care and early ripening, it deserves the attention of summer residents and gardeners. Subject to competent agricultural techniques and proper storage conditions, you can use this useful vegetable throughout the year, replenishing the body with valuable elements and strengthening its defenses to resist disease.