Gourds, such as melon, love heat, so they were grown in the middle lane in greenhouses. But, given the many years of selection work of scientists, new varieties have appeared that grow and bear fruit in the open ground. Today's article about these crops and the intricacies of growing melons in open beds.
Varieties of melons for growing in the suburbs
It is a long winter in the Moscow Region, the soil thaws completely at the end of April, and return frosts recede around mid-May. Summer lasts about 3.5 months, but in August the night temperature drop already begins. Therefore, melons with early and medium ripening periods are suitable for planting in this region.
The following varieties are especially popular:
- Pineapple F1. Mid-season, oval-shaped fruit, weighing up to 2.5 kg, dense yellow-orange peel with a mesh pattern. The pulp is yellow, juicy and sweet, slightly oily, a wonderful aroma with notes of pineapple. Melon is resistant to anthracnose and pests, transportable and perfectly stored;

- Golden. Medium early culture, resistant to temperature extremes. The color of the peel corresponds to the name, the flesh is white, fragrant, sweet. The weight of the fetus is up to 2 kg; during transportation, it retains its presentation. It is immune to disease;

- Collective farmer. Mid-season, spherical berry of medium size, weighing up to 1.3 kg. The peel is bright yellow with a chaotic light hatching. The flesh is creamy color, dense fibrous structure, crisp, sweet. Transportability is excellent, but prone to fungal diseases;

- Lolita. The mid-early berry is round in shape, saturated yellow with interspersed spots and stripes. Melon weight up to 2 kg. The taste of pale yellow pulp is delicate, moderately sweet. Resistant to temperature changes;
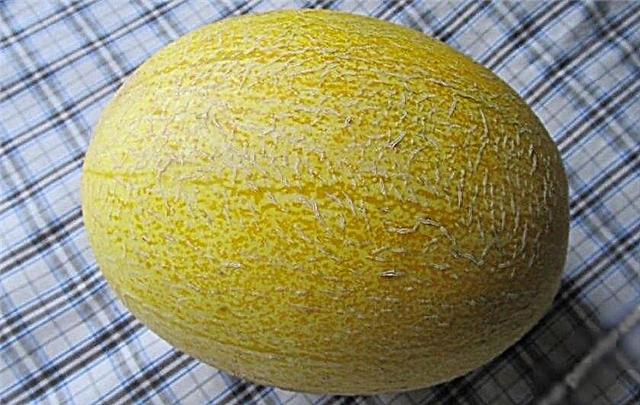

- Tender. The mid-early ripening period is round, the fruit is divided into longitudinal segments. The main color is yellow, the dividing lines of the segments are greenish, brighten at the stage of full ripening. Weight up to 1.1 kg. Fine-grained, light green pulp juicy with a sweet taste;

- Augen F1. Mid-season, high-yielding. Valued for its resistance to most fungal diseases and high palatability. The weight of the berries is on average 1 kg. The pulp is dense, poured with juice and sweetness;
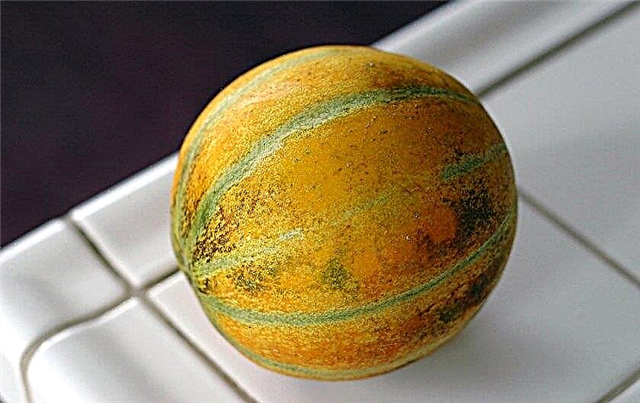

- Princess Svetlana. The average ripening period, the shape of the fetus is rounded with slightly expressed segments, the peel is smooth, white. Highly resistant to anthracnose and powdery mildew, temperature extremes. The pulp is light, sweet-juicy, tightly crisp, with a pronounced aroma;

- Charlotte. Medium early melon, similar to a bright orange ball. The peel is thin with a smooth surface, the fruit weighs 1.7 kg. The pulp has a high content of sweetness and carotene, a strong melon aroma, the color of the pulp matches the peel. The variety tolerates long transportations.

Advantages and disadvantages of planting melon in open ground
The method of growing gourds in an unprotected area has its pros and cons.
- Main advantages:
- saving money and time for leaving;
- full lighting, no fuss with lights;
- there is no need for ventilation and humidity control;
- to put trellis support on the site is cheaper than building a high greenhouse;
- no need for artificial pollination;
- in a ventilated area, plants are less susceptible to infection by fungi than in a greenhouse environment with high humidity.
- Disadvantages of unprotected soil:
- weather conditions (frost, frequent rains, gusty wind);
- the presence of pests.
Preparation for landing
Before planting, it is important to prepare the seeds for growing seedlings, to ensure proper care, to select the soil composition and location on the site.
Did you know? There are varieties of melons that are sold at auction for an amount of 20 thousand dollars or more. For example, Yubari King melon, grown only in Japan.
Semen
The first thing to note when choosing planting material is the reputation of the manufacturer. It is recommended to purchase goods from well-known companies or private farmers. Save on buying is not worth it: quality material has an appropriate price.
When buying, you should inspect the packaging for leaks, make sure that the seeds are suitable. Expired grains are unlikely to sprout; opened or damaged packaging also does not guarantee the quality of the material. The shelf life of gourds is approximately 3 years, depending on the storage conditions.
 Be sure to check with the seller for information on recommended growing regions, if the variety is zoned
Be sure to check with the seller for information on recommended growing regions, if the variety is zoned
Own seeds and purchased without preliminary processing need preparation for planting. Sequencing:
- Soak for 20 minutes in a bright pink solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection. At the same time, the pop-up dummies are immediately discarded.
- Then rinse and wrap in a damp cloth. Leave warm for 12 hours (+ 21 ... + 24 ° С), regularly wetting the parcel.
- The swollen seeds need to be hardened: put on the refrigerator door in a temperature condition of -3 ° C, for 2 days.
- Then the material is laid out on a dry material in heat for germination.
Important! The procedure for hardening planting material is required for the Moscow region and regions with a similar climate.
Seedlings
Melon does not tolerate transplanting from place to place, so it is recommended to grow seedlings in peat pots, which can be placed in the ground with the plant. It is better to prepare the soil for sowing yourself, for this, take the following components:
- high peat - 9 parts;
- sand - 1 part.
The mixture must be steamed or preheated in an oven at 100 ° C for disinfection. Then to 10 l of base add 200 g of wood ash, potassium fertilizer 15 g, phosphate fertilizer 30 g. A light drainage is placed on the bottom of the pot: pieces of bark. The soil is covered with layers, spilling to compact.

Sowing is carried out about a month before the intended landing in the ground. Seeds are placed in the soil to a depth of 3 cm. Crops are covered with a film, until seedlings appear they provide a temperature of + 25 ... + 30 ° С.
Sprouts appear within 5-8 days. Sprouted shoots are freed from shelter and placed on the southern windowsill. If additional lighting is required, a phytolamp is used.
 When several sprouts appear in one pot, the weak ones must be removed, but not tearing from the ground, but pinch the stem above the soil
When several sprouts appear in one pot, the weak ones must be removed, but not tearing from the ground, but pinch the stem above the soil
After the appearance of 3 leaves, the stem must be pinched. This is necessary in order to set the correct formation of the plant lashes. Subsequently, as the bush grows, the procedure is carried out several more times.
When watering, its frequency is regulated, focusing on the state of the soil. Excessive moisture can cause decay of the sprouts. Seedlings do not need to be fed, as food was laid in the ground.
Planting melon seedlings in open ground
The grown seedlings are planted in soil warmed up to + 15 ° C, approximately in the second half of May. At this time, the bush already has up to 4 strong leaves and the direction of growth of the lashes. The precursors for melon are root vegetables, leafy vegetables, legumes and all kinds of cabbage
The precursors for melon are root vegetables, leafy vegetables, legumes and all kinds of cabbage
Seat selection
The place on the site should be as light as possible, protected from the winds, the south side is better. Nearby, the location of tall shrubs or trees is not desirable, the shadow negatively affects the development of melons. The plant does not like the accumulation of water, so the place should be flat or sloping, but not in the lowland. The distance from the surface of the groundwater is at least 2.5 m.
Soil preparation
In the fall, the plot is removed from the plant residues of the previous crop. Dig a shovel on a bayonet, introducing 4 kg of humus, 30 g of superphosphate and potassium salt per m². If the soil is acidic, which is bad for melon, add wood ash 300-600 g / m². Dense and heavy earth is “diluted” with sand, approximately 1.5 kg per m².

In the spring, 2 weeks before planting, they dig a trench and warm its bottom with dry plant debris, sprinkle a little soil on top and fertilize with 30 g / m² ammonium nitrate. Vegetation will rot, releasing heat and nutrients. For good soil warming, the trench is covered with a film.
Important! In the spring, fresh manure should never be added to the planting pit: it will burn the root system.
Landing technology
Since gourds build up long lashes, you need to take care of the support in advance. The most convenient way to garter on a trellis. On the 4th day after planting, the seedlings are sent to the trellis and tied as they grow. This method allows all lashes to be evenly lit and warmed up by the sun.
In the prepared trench, plants are planted at a distance of 50–70 cm from each other. A little water is poured into the formed holes, waiting for it to settle. The bush is placed in a hole without deepening the growth point, it remains above the surface. Water for irrigation must be used warm not lower than + 18 ° С.
Further care
The melon bush must be formed in order to achieve maximum returns. To do this, pinch it as it grows, leaving 2-3 lashes. The number of fruits is also standardized; 3-5 fruit ovaries are left on one bush. As a consequence, pinch and shoots over the fruits so that they do not delay the nutrition.
Soil care
Aisles and the space between the bushes should be clean from weeds. Herbs parasites inhibit cultural plantings and create increased humidity, which in turn attracts fungal spores. The root system of gourds should be regularly saturated with oxygen. The tree trunk circle is loosened to a depth of 10 cm. To protect the stems from overheating, bushes are spudled according to the example of potatoes.
The root system of gourds should be regularly saturated with oxygen. The tree trunk circle is loosened to a depth of 10 cm. To protect the stems from overheating, bushes are spudled according to the example of potatoes.
Watering
Young bushes are watered daily in small portions - 0.5 l under the bush. Water should not stagnate, do not fall on foliage. As the bush grows, the water norm is increased, and with the onset of flowering, the interval is reduced to a time of 3-5 days. The hydration of the crop is completely eliminated 2 weeks before harvest.

Fertilizers
During the growing season, the melon is fed about 3 times:
- the first - 14 days after planting, mullein infusion diluted with water (1:10);
- second - during the flowering period, 200 g of wood ash is diluted in 10 l of water;
- third - at the beginning of fruiting, 10 g of saltpeter, 20 g of potassium chloride, 50 g of superphosphate are taken per 10 l of water.

Protection against diseases and pests
Preventive measures against diseases and insects are seedbed preparation, soil disinfection. Next, you need to observe crop rotation, clean the soil and monitor the norms of watering and top dressing. Such a simple procedure as loosening the soil destroys the larvae of harmful insects.
Familiarity with measures to combat diseases and parasites will not be superfluous:
- Aphid - dangerous for foliage and stems. Destroy it with a solution of karbofos 60 g / 8 l of water or spraying with a soap solution of 100 g of grated chips per 10 l of water.
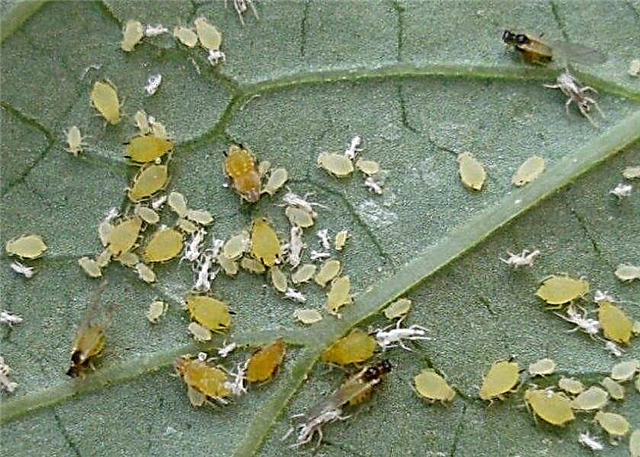 Parasitizing, the insect eats green mass juice, this leads to curl of the leaves and their slow withering
Parasitizing, the insect eats green mass juice, this leads to curl of the leaves and their slow withering - Spider mite - destroys the green parts of the plant. Effectively using the drug "Agrovertin" 2 ml / 1 liter of water, spray the entire bush.
 Affected melons gradually turn yellow and die
Affected melons gradually turn yellow and die - Scoop - a gnawing insect destroys greenery, flowers and ovaries. Against it, spraying with the Decis preparation is used 1 g / 10 l of water.

- Fusarium, gray rot - against fungi, a solution is prepared from a mixture of substances: zinc sulfate 1 g, copper sulfate 2 g, urea 10 g. The mixture is diluted in 10 l of water.

- Powdery mildew - spend spraying with a solution of colloidal sulfur, prepared in a ratio of 100 g / 10 l of water.

Harvesting and storage
Depending on the variety, the harvest of melons and gourds begins at the end of July or in August. The fruits ripen unevenly, so harvesting can stretch out. Berry maturity is determined by external signs:
- skin color corresponding to the variety description;
- the presence of dry cracks on the surface of the peel;
- easy separation from the whip;
- pronounced aroma.

Remove the berry from the bush with a part of the stalk, approximately 2-3 cm, thus extending its shelf life. Shelf life of different varieties from 1 to 6 months. For normal storage, an acceptable mode should be provided:
- temperature + 4 ° С;
- humidity 70%.
To grow a melon on unprotected soil in the climatic conditions of the Moscow region is a strength and a beginner. Compliance with agricultural technology and competent planting care will provide a large and tasty crop.Did you know? In Central Asia, an unusual variety of melon Cucumis microcarpus is grown, which tastes like strawberries.









 Parasitizing, the insect eats green mass juice, this leads to curl of the leaves and their slow withering
Parasitizing, the insect eats green mass juice, this leads to curl of the leaves and their slow withering Affected melons gradually turn yellow and die
Affected melons gradually turn yellow and die