In domestic areas, different varieties of quince are often found. Thanks to this plant, you can decorate the garden, make an unusual hedge, and even enjoy fruits rich in vitamins and minerals. One of the most beautiful cultures is considered Japanese quince or Japanese henomeles. This article will consider not only popular varieties for the Moscow region, but also the technology of their cultivation.
Description and features of the culture
Japanese quince is considered a tall shrub. On the surface of the plant are frequent and large leaves of elongated shape. The leaf plate is characterized by a rich green tint. Plant height - up to 3 m.
Detailed crop description:
- young shoots are green, scaly-felt, and with age they become naked with a brown color;
- the length of the leaves is 3–6 cm, and the width is 2–4 cm;
- flowers - pink, orange or red;
- inflorescences are large, thyroid;
- the width of the flowers is up to 5 cm. They form an inflorescence, collecting 3-5 pieces;
- roundish fruits with yellow-green peel. The diameter of the fetus is up to 6 cm. Quince is suitable for consumption.
Berries ripen closer to October. Japanese quince belongs to slow-growing crops. Despite the fact that the plant is considered thermophilic, it is able to survive frosts up to -30 ° C. Fruiting occurs in the fourth year after planting in open ground. Productivity is average, about 3 kg of fruits are harvested from each tree.
Important! Due to its overly tart taste, fresh fruits are rarely eaten. They are mainly used for making jam, compote and jam.
Varieties for growing in the suburbs
The following varieties of Japanese quince are often grown in the Moscow Region:
- Nivalis - This is a powerful plant, the height of which is up to 1.5 m. The flowers are white and the leaves are covered with velvety bloom;

- Simony (Simonii) - shrubs are covered with a large number of large leaves. The height of the plant is not more than 1.3 m. The flowers are dark red in color, which is characteristic of most varieties of Japanese quince. The fruits are large, yellow-green;

- Geisha Girl - bush height up to 1.5 m. It is covered with double flowers of delicate cream color;
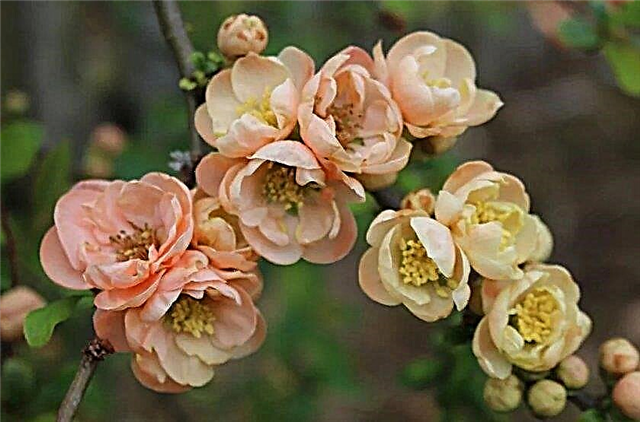

- Pink Lady - Slow-growing shrub, the height of which is not more than 1.4 m. Pink flowers. This variety is able to tolerate severe frosts (up to -35 ° C) and grow in the shade. Therefore, it is ideal for cultivation in the central regions of the country;

- Fascination - A wide bush, up to 1.5 m high. Purple flowers gathering in inflorescences.

Quince planting in open ground
To grow a beautiful and fruitful plant, you will need to properly plant. First of all, choose a high-quality seat to make the quince feel comfortable. You should also choose a healthy seedling. This is best done in specialized nurseries in order to purchase planting material that is resistant to frost, disease and pests. On the surface of the seedlings there should be no spots, deposits and cracks. Their presence can lead to the fact that the plant does not take root well.
Did you know? During the Tudor rule, quince was made from quince, which was considered a powerful aphrodisiac.
Landing time
It is necessary to plant Japanese quince in the spring, when the soil warms up to + 10 ° C. The ambient temperature should be from + 15 ° C to + 17 ° C. Best plant survives if planted in the morning or evening, when there is no active sunlight. This can lead to burns on the crown. If you plant a Japanese quince in the fall, it can negatively affect its development. Young plants do not have time to take root before the onset of frost and freeze.
Seat selection
It is necessary to plant Japanese quince in sunny areas. In the shade, shrubs grow poorly and the flowering process is disturbed. Try to plant crops in places that are protected from northerly winds and drafts. Japanese quince prefers to grow on loamy soils with low acidity. Optimum pH balance - no more than 6.

Soil preparation
Since culture prefers to grow on nutritious and fertile soils, it is necessary to prepare a seat in advance. First, the site must be carefully watered so that the soil is moistened to a depth of 40 cm. After that, add organic fertilizers (rotted manure or peat) in an amount of 20 kg per 1 m².
After 2-3 days, when water and nutrients penetrate the inner layers of the earth, you can begin to mark the garden. Dig holes 60 x 60 cm in size. The distance between the bushes should be 1.5 m. If you are going to grow Japanese quince as a hedge, then keep the distance between the bushes at 80 cm.
Add 10 kg of humus and 500 g of wood ash to the dug pit. Then add about 5 kg of garden soil and mix all the ingredients thoroughly. When all the actions have been completed, proceed with the planting procedure.
Landing rules
A step-by-step landing procedure is as follows:
- Place planting material inside the hole so that the root collar remains above the surface of the soil.
- Sprinkle the roots of the plant with earth and pour enough water (at least 10 liters).
- Make a small depression around the shrub where water for irrigation will be poured.
- Cover the basal part with a layer of mulch (peat, chopped tree bark or sawdust), at least 10 cm high.

Care
They will delight you with delicious and fragrant fruits. The main stage of care is watering. This is due to the fact that Japanese quince is hygrophilous. Particular attention should also be paid to top dressing, pruning and frost protection. It is important to loosen the topsoil in time and remove weeds.
Watering
Particular attention should be paid to watering in dry weather. In such periods, pour at least 30 liters of water under each bush so that the soil is moistened to the required depth. If rainy weather prevails, then the plant does not need additional moisture. After irrigation, the topsoil should be loosened to a depth of 8 cm so that the roots do not rot. If desired, you can water the crown of the bush to make the leaf plates more vivid.
Important! Weeds must be removed every week to reduce the risk of pests.
Fertilizer and fertilizer
Given that the gardener must fertilize during planting, the first year will not require fertilizer. All dressings are introduced, starting from the second or third year after planting.
The steps in the procedure are as follows:
- In the spring, 300 g of superphosphate and 150 g of potassium nitrate are added to each bush.
- In summer, use ammonium nitrate (20 g per plant).
- In autumn, pour 3 liters of mullein solution (90 g per 10 liters of water) under each bush.

Pruning
Culture needs both sanitary and formative scraps. Both procedures are carried out in the spring, before the sap flow in the branches. If the gardener adheres to the optimal timing of pruning, he will be able to maintain the quality of inflorescences and yield indicators.
The formation of the crown is that remove branches that are out of shape. They should be cut only 2/3, and the cut points should be treated with garden var. This will help prevent the development of parasites, as well as not disrupt the structure of the bush. During sanitary scraps, dry shoots damaged by snow and frost are removed.

Winter preparations
Despite the high frost resistance of the culture, it is necessary to cover the bushes for the winter. This is especially true for young plants that have not yet had time to strengthen and form the immune system. Cover the trunk circle with a dense layer of fallen leaves, spruce branches or bark. The height of the mulch should be about 25 cm. The procedure is recommended to be carried out 2-3 weeks before the onset of frost.
Did you know? Peoples living in the Mediterranean consider quince a sign of Venus. It is believed that this culture is a symbol of love and fertility.
Diseases and Pests
Japanese quince shrubs can be affected by diseases such as cytosporosis and ramulariosis. Symptoms of these diseases are manifested in the fact that the leaves acquire a brown color, and the color of the bark becomes less saturated. To protect the genomeles, it is necessary to spray with the Aktara solution (40 g per 10 l of water). The treatment interval should be no more than 2 weeks, so that the bacteria do not have time to recover and multiply.

Among the frequent pests, scabbard and spider mite should be noted. Against them, it is advisable to use strong chemicals. In the fight against scale insects, a solution of Karbofos (40 g per 10 l of water) is used. Against the spider mite, Actellik is used (30 g per 6 liters of water). Spraying is carried out 1 time per month. This will be enough not to harm the plant, but not to allow the parasite larvae to develop.

Breeding
Many gardeners use different methods of propagating quince gardening, depending on the capabilities and skills. In total there are several ways to breed culture:
- cuttings;
- using seeds;
- vaccinations;
- dividing the bush;
- layering.
Cuttings
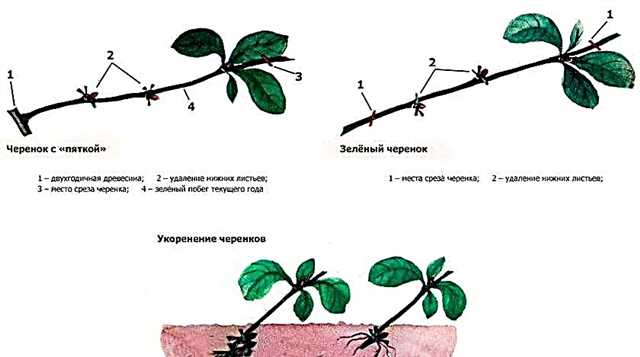
The most common method of propagation is considered to be cuttings. Thanks to him, all varietal qualities of the culture are preserved. It is necessary to harvest cuttings in dry weather, best in hot summers. Cut small shoots from an adult plant (2-3 years) so that on each branch there is a heel (last year's wood), up to 1 cm long.
In order for the plant to take root, it is necessary to soak it in the Kornevin solution (50 g per 5 l of water). It is necessary to maintain in this state for at least three days in order to stimulate growth. After that, prepare a nutrient substrate, mixing peat and sand in a ratio of 1: 3. Deep green cuttings into the soil at an acute angle.
After about 30 days, when the root system is slightly developed, transplant the culture to a permanent place. To protect the culture from winter frosts, cover the bushes with agrofibre or plastic wrap. Remove shelter in the spring, so as not to provoke the development of fungal infections.
Seeds
Many gardeners are convinced that breeding quince with Japanese seeds is the most reliable way. This is due to the fact that the germination rates of henomeles are high, about 80%. Sowing is carried out at the onset of winter, and by mid-March, the first shoots will appear.
Preparing and planting seeds consists of the following steps:
- Pour them with warm water. An empty seed pops up, after which it must be discarded.
- Wrap suitable seeds in cheesecloth and refrigerate on the lower shelf. There they must be stored for at least 30 days.
- Transfer the seeds to a bag of wet sand and leave in this position for 50-60 days.
- Sow the seed with the onset of spring, deepening by 50 cm.

Through vaccination
Often gardeners resort to reproduction through vaccination. As a stock, a seedling of the main species is used. The graft is a varietal shank. In mid-August, when there is an active sap flow in the soil, an eye vaccination is performed.
The essence of the procedure is as follows:
- In the middle of the varietal cuttings, cut a healthy kidney along with part of the bark.
- Make a small incision on the rootstock.
- Bend the edges of the "wound", place the kidney inside and wrap it back.
- Wrap the cut area with film or cloth so that the eye is open.
- After 20-30 days, the eye will take root.
- Transplant to a permanent place next year when an escape is formed in place of the kidney.
- Care is that every week you need to spray the eye with clean water.

Division
Genomeles is characterized by a developed root system. Therefore, many gardeners prefer to propagate the culture by dividing the bush.
The technology is as follows:
- Dig up an adult plant.
- Take root offspring, about 15 cm long and 0.5 cm thick.
- Transplant them next to the mother plant, deepening by 10 cm.
- Regularly water young plants, and immediately after planting, cover with a 10-centimeter layer of sawdust mulch.

Layering
Japanese quinces often have creeping shoots that can be cut off and used for cultivating varieties. Dip them next to the mother plant, not separating from the main bush. Cover with a layer of mulch and water every week. After the time when the root system is developed (usually takes at least 3 months), it is possible to separate the layers from the mother bush and transplant to a permanent place.

When it matures and how to harvest
The fruits ripen in September or October, depending on weather conditions and the quality of care. Their peel is covered with a dense layer of wax coating, which protects quince from damage by pests. If the fruits have not yet ripened, then they still need to be harvested before the onset of frost. If you place them in a room where the air temperature is from + 3 ° C to + 5 °, they will be able to ripen. You need to collect the fruits of Japanese quince in dense boxes and arrange them so that they do not fight against each other. Otherwise, the crop will not be stored for a long time and will begin to rot very soon.
So, now you know that it is not difficult to grow Japanese quince if you follow the basic rules for planting and care. Thanks to simple actions, you can enjoy aromatic fruits from which delicious desserts are made in 3-4 years.

















